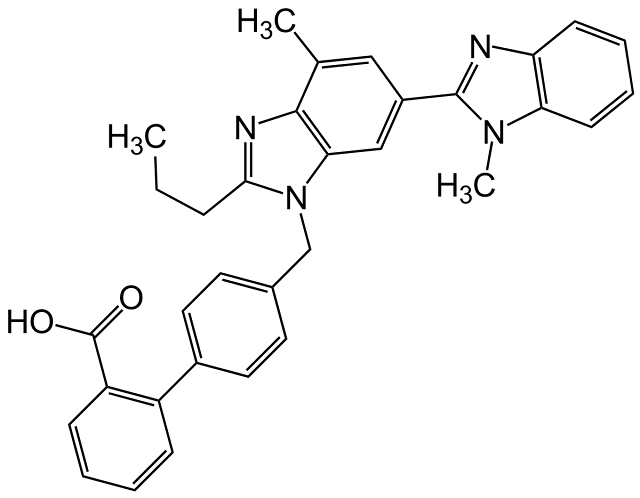
Telmisartan Is A Common Medication Used To Treat High Blood Pressure
Telmisartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). It lowers blood pressure by blocking the action of certain natural substances that tighten the blood vessels. It is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). It can help lower risk for heart attack and stroke. It can also help to keep kidneys working well. When blood pressure is high, it can damage the heart and kidneys and increase risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
It works by relaxing blood vessels so that the heart can work more efficiently and the blood can flow more smoothly to different parts of the body. It also lowers the level of salt and water in blood, which helps prevent the buildup of fluid in the lungs and kidneys.
The size of the worldwide Telmisartan Market, which was estimated at US$ 3,880.9 million in 2017, is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 1.4% from 2018 to 2026.
It is available as 20, 40, and 80 mg tablets. The tablets are usually swallowed whole without chewing or crushing them. The tablets should be stored at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
It is a renin angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor, which means that it blocks the action of the hormone angiotensin II on special receptors in the body. Angiotensin II normally causes the peripheral blood vessels to narrow, and it also stimulates the production of another hormone called aldosterone.
Telmisartan is metabolized by conjugation to form a pharmacologically inactive glucuronide that is removed from the body via urine. This glucuronide has no effect on plasma concentrations of angiotensin II, renin, or aldosterone and does not have a clinically significant impact on electrolytes.
It is a member of a class of medicines called angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). These medications lower blood pressure by blocking the action of a chemical called Telmisartan that causes the walls of blood vessels to tighten or constrict. A high blood pressure may lead to a heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, and other serious problems.
It has the shortest half-life among ARBs, resulting in rapid and sustained reduction of blood pressure. This is a major advantage over other ARBs such as valsartan, which typically requires a daily oral dose to achieve significant antihypertensive activity.
Control of the early morning blood pressure surge is also an important clinical advantage of Telmisartan. Other benefits include reduced plasma cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and triglyceride concentrations. In addition, it is able to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in people with type 2 diabetes. It is also useful in lowering blood pressure in people with kidney disease or a history of heart failure.


Comments
Post a Comment