Bile Duct Cancer; a Rare Form of the Cancer That's Found Anywhere in the Bile Ducts
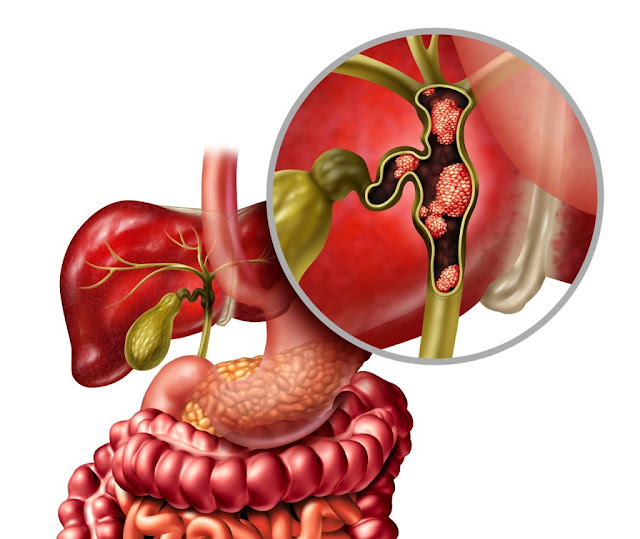
Bile Duct Cancer (also known as cholangiocarcinoma) is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the bile ducts. Nearly all cholangiocarcinoma are cholangiocarcinoma. These cancers are a type of adenocarcinoma, a cancer that starts in gland cells that line the inside of the ducts.
Cholangiocarcinoma is a type of cancer that develops in the bile ducts, the tubes that carry bile from a liver to the intestine. It is rare, but there are some risk factors that increase the chance of developing cholangiocarcinoma. It can usually only be cured if cancerous cells haven't spread.
The Bile Duct Cancer Market is anticipated to reach US$ 185.4 million in 2021 and grow at a CAGR of 12.8% during the projected period (2021-2028).
A doctor will diagnose cholangiocarcinoma by doing a physical examination and reviewing a medical history. People also need imaging tests and scans to confirm the diagnosis. The extent of cholangiocarcinoma is an important factor in deciding on treatment options.
Whenever possible, a surgery is the main treatment for cholangiocarcinoma. It offers the only realistic chance for a cure. Only the small proportion of cholangiocarcinoma cases are diagnosed early enough to be suitable for surgery. This is because symptoms usually develop at a late stage.
In biomedical research, microbiological research, the diagnosis of chlamydia, hepatitis, herpes simplex, HIV, and influenza infections, as well as the treatment of diseases like cancer, Monoclonal Antibody Diagnostic Reagents are crucial diagnostic tools.
There are 4 stages of cholangiocarcinoma, from stage 1 to stage 4, which entirely depends on the type of cancer people have. Stage 1 means the cancer is small. Stage 2 means that the cancer is larger.
Stage 3 means that the cancer has spread to nearby blood vessels, tissues, organs, and lymph nodes and stage 4 means that the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. While, the grading system divides Bile Duct Cancer into 3 grades, from 1 to 3. Grade 1 means the cancer cells look similar to normal bile duct cells. Grade 2 means the cancer cells look a bit abnormal.
Grade 3 means a cancer cells look very abnormal and unlike normal bile duct cells. In April 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Pemazyre (pemigatinib), the first targeted treatment for patients with cholangiocarcinoma, a cancer of bile ducts.


Comments
Post a Comment