Fractional Flow Reserve Measurements Are Used For Measuring Blood Pressure and Flow in Coronary Arteries and Are Performed Under Sedation
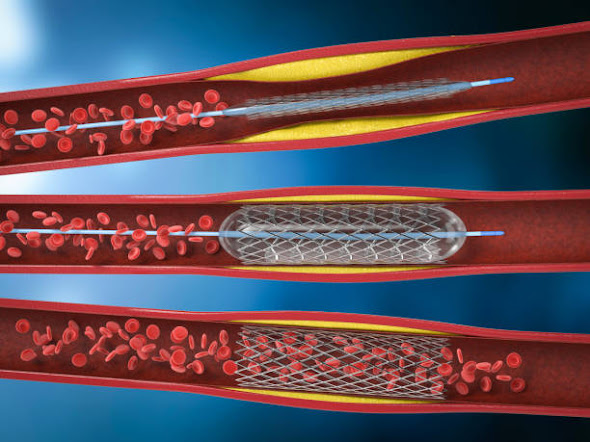
The Fractional Flow Reserve is a measurement of blood pressure and flows in a coronary artery. It is performed with the help of a guide wire through a standard diagnostic catheter during a coronary angiogram. It is used to determine if angioplasty or stenting is needed to open up a coronary artery and increase blood flow to the heart. If a patient has a high FFR, the procedure should be considered.
Several studies have compared the Fractional Flow Reserve with angiography. While invasive coronary angiography is the gold standard for functional assessment of coronary artery disease, noninvasive fractional flow reserve has emerged as an effective adjunct to the invasive procedure. Furthermore, it has shown high diagnostic accuracy, may improve patient outcomes, reduce health care costs, and increase patient quality of life. Current approaches include full-order and reduced-order computational fluid-dynamic models, as well as artificial intelligence-based deep machine learning algorithms.
A new test called FFR was developed to determine the functional importance of coronary stenosis. The FFR is a quantitative measurement of coronary artery pressure. It is used to identify patients who will benefit from coronary revascularization. However, it is important to understand that the FFR does not measure the actual blood flow within the coronary artery. The FFR does not account for the pressure of the aortic valve. The Fractional Flow Reserve Market measurement is used to determine the severity of coronary stenosis. It helps to determine treatment options by using antegrade and collateral flow. FFR measurements are accurate even in patients with chronic myocardial infarction. It also saves patients money by reducing the use of contrast media and other diagnostic procedures. And, FFR is also a valuable tool for identifying patients with intermediate or high stenosis.
A Fractional Flow Reserve measurement is performed under sedation by a physician. In the procedure, the patient lies flat on the operating table while the physician inserts a thin guide wire. He then injects a medicine into the blood vessel. This increases blood flow. The flow and pressure are measured with a monitor and the doctor can then see the results. In November 2021, MMCSC (Monmouth Medical Center Southern Campus) announced the availability of a technology called FFR-CT (Fractional Flow Reserve Computed Tomography, which evaluates the blood flow through the arteries to determine presence of blockages and their location.


Comments
Post a Comment